Bronchial asthma is a serious respiratory condition marked by wheezing, chest tightness, and persistent coughing. If ignored, it can lead to severe problems, endangering well-being. The chronic ailment narrows air passages, complicating breathing and posing life-threatening risks. Recognizing bronchial asthma symptoms and their severity emphasizes the need for proactive management. Let’s explore bronchial asthma’s intricacies, delving into bronchial asthma causes, symptoms, and vital steps for effective relief.
What is Bronchial Asthma?
Wondering about bronchial asthma? It’s just a term for asthma, a persistent inflammatory condition affecting airways, causing intermittent bouts of coughing, wheezing, breathlessness, and chest tightness. The CDC notes over 25 million Americans, including 6.8 million kids, grapple with asthma. Allergies play a significant role, connecting to conditions like chronic sinusitis, ear infections, and nasal polyps. Those with both asthma and allergies often experience night awakenings, work disruptions, and reliance on potent medications.
Bronchial asthma symptoms:
- Shortness of Breath: Individuals with asthma often experience difficulty in breathing, especially during physical activities or exposure to triggers.
- Coughing: Frequent nighttime or early morning coughing is a prevalent sign of bronchial asthma, indicating the condition’s impact on daily life.
- Wheezing: A whistling or squeaky sound during breathing is indicative of constricted airways.
- Chest Tightness: Sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest, contributing to discomfort.
- Fatigue: The effort required to breathe in asthma can lead to fatigue and overall weakness.
Bronchial Asthma Causes:
- Atmospheric Dust: Airborne dust can irritate the airways, causing bronchial asthma symptoms such as coughing and wheezing. Protect yourself with proper ventilation and cleaning.
- Viral Illness: Common cold or flu viruses can worsen asthma, potentially causing severe attacks. Guard against respiratory infections to manage asthma effectively.
- Bacterial Illness: Respiratory tract bacterial infections can escalate bronchial asthma symptoms, heightening the likelihood of flare-ups. Guard against infections to maintain asthma control.
- Flu: Influenza viruses can significantly impact individuals with asthma, causing respiratory distress and potentially triggering severe asthma attacks.
- COVID-19: The COVID-19 virus, especially in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma, can lead to severe complications and exacerbate asthma symptoms. It’s crucial for asthma patients to take extra precautions to reduce the risk of exposure to COVID-19.
- Pet Allergy: Furry friends bring joy, but for asthma, they trigger wheezing. Manage symptoms and create a hypoallergenic haven at home.
What is the Mechanism Behind Bronchial Asthma?
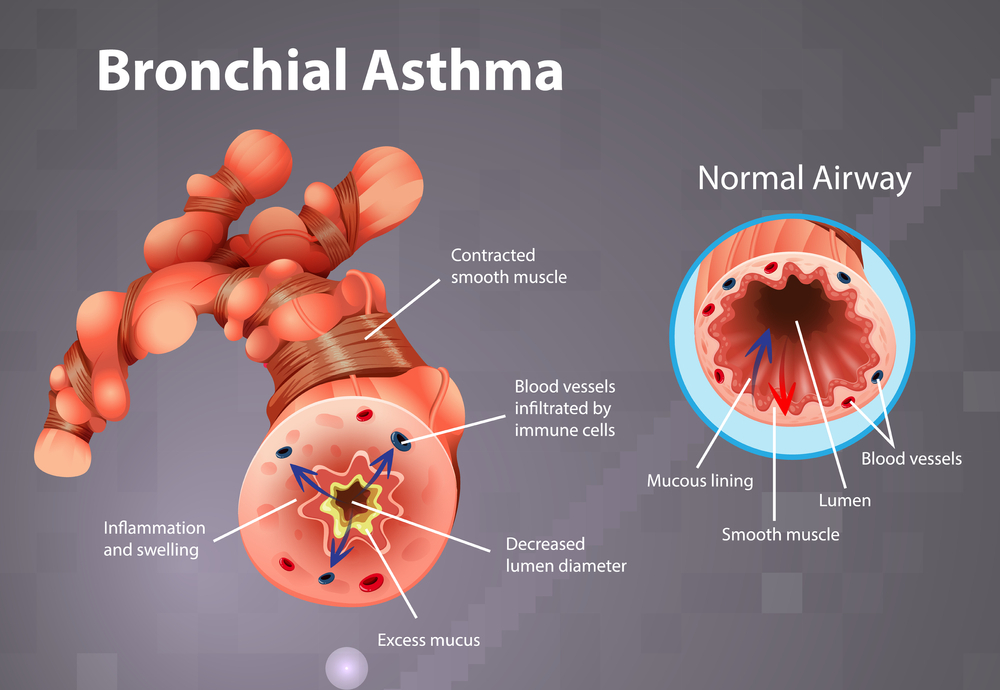
Bronchial asthma’s mechanism involves the inflammation of airways, triggering excessive mucus production and the narrowing of bronchioles. This inflammation results from the immune system’s hypersensitive response to various stimuli. Persistent coughing, a hallmark bronchial asthma symptoms, arises as the airways struggle against constriction. The smooth muscles surrounding the bronchi contract, causing breathlessness and wheezing. Environmental factors, genetics, and respiratory infections contribute to this intricate process, making bronchial asthma a complex interplay of immune responses and physiological changes within the respiratory system.
Bronchial Asthma Diagnosis:
Early and accurate bronchial asthma diagnosis is crucial for managing bronchial asthma effectively. Several diagnostic tests aid in confirming the presence of asthma and determining its severity:
- Feno (Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide): Measures the level of nitric oxide in the breath, helping to identify airway inflammation.
- Spirometry: Assesses lung function by measuring the amount and speed of air exhaled. This test can reveal airflow limitations characteristic of asthma.
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE) Levels: Elevated IgE levels in the blood may indicate an allergic component triggering asthma symptoms.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Detects signs of inflammation, infection, or allergic reactions.
- Allergy Testing: Identifying specific allergens through skin tests or blood tests helps in understanding and managing triggers.
How to Prevent Bronchial Asthma:
Taking proactive steps is crucial in bronchial asthma management. Lifestyle changes can markedly decrease asthma attack frequency and severity. Here are some preventive measures:
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity enhances respiratory muscles and lung function. Opt for asthma-friendly exercises and consult a healthcare professional before beginning any new workout routine for safety.
Avoiding Triggers: To reduce asthma attacks, recognize and avoid triggers like allergens or pollutants. Adjust your living environment and wear protective gear when necessary.
Proper Medication Adherence: Consistent use of prescribed medications, including inhalers and oral medications, is vital in controlling bronchial asthma symptoms. Skipping doses or self-adjusting medication without consulting a healthcare provider can lead to exacerbations.
Maintaining Clean Indoor Air: Regularly cleaning and maintaining HVAC systems, especially air conditioning units, can significantly reduce the presence of airborne irritants. Changing filters and cleaning ducts at least every six months can create an environment less conducive to asthma triggers.
Regularly cleaning air conditioning units is a crucial preventive measure. Because it accumulated dust, mold, and allergens in AC systems contribute to indoor air pollution. Consistent maintenance, including filter, coil, and vent cleaning, ensures clean and trigger-free circulated air, significantly preventing asthma exacerbations.
Conclusion:
Bronchial asthma demands vigilant awareness and proactive management. Recognizing its symptoms, mechanisms, and diagnostic methods is crucial for effective bronchial asthma treatment planning. Embracing preventive measures, from regular exercise to clean indoor air maintenance, significantly enhances the quality of life for individuals grappling with this intricate respiratory condition. Through education and proactive care, we empower ourselves and others to breathe easier in the face of the challenges posed by bronchial asthma.
Related Blog: Allergic Asthma: About Causes, Symptoms, Tests & Treatment

