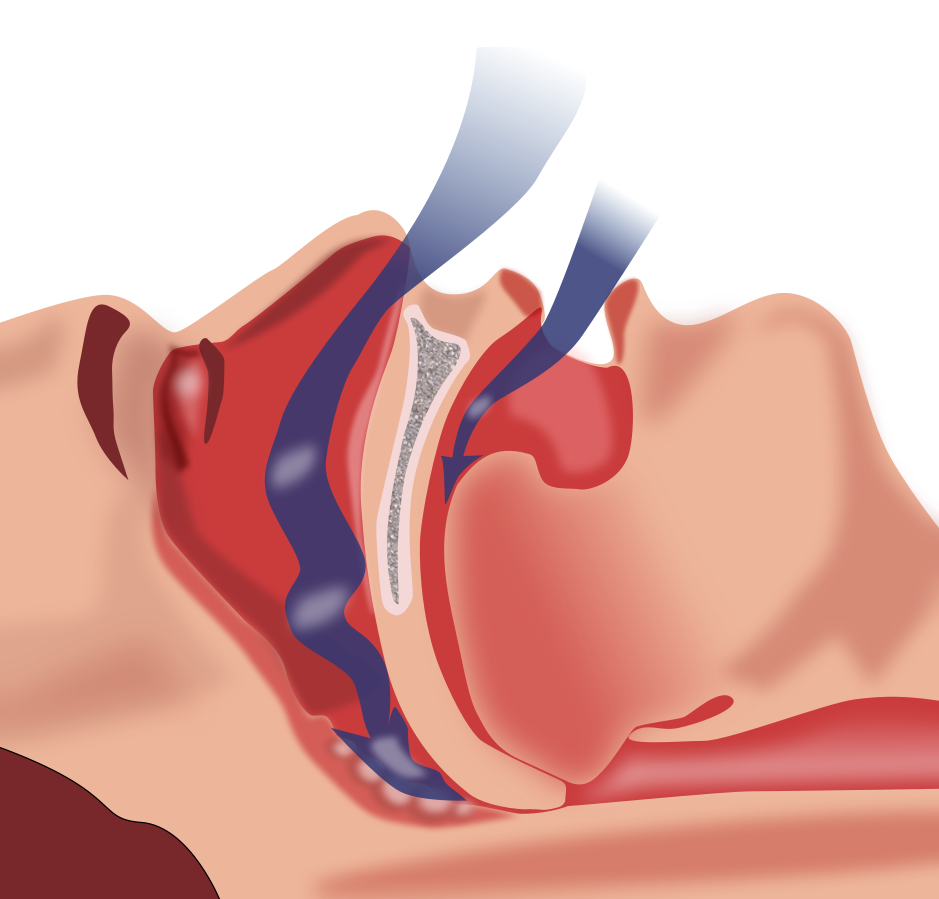
Diagram of how a person’s airway is constricted by obstructive sleep apnea. Image credit: Wikimedia Commons.
Did you know that approximately 5 to 10 percent of people struggle with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)? This common yet often challenging sleep disorder can have significant impacts on daily life and long-term health. From feeling perpetually tired to facing serious health risks, understanding obstructive sleep apnea is crucial for both the individuals affected and their loved ones.
What Is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea is a prevalent sleep disease where your breathing continuously stops and starts during sleep. It happens when your throat muscles relax, causing your airway to narrow or close off momentarily. This interruption in breathing can lead to snoring, choking, and fragmented sleep. Those people who have obstructive sleep apnea, they often feel tired during the day and may experience other health problems if it’s left untreated. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, CPAP machines, or surgery.
How Does Obstructive Sleep Apnea Make You Feel?
Living with obstructive sleep apnea means facing a relentless struggle with fatigue and lethargy. Many people with OSA experience symptoms like snoring and daytime sleepiness.:
- Lethargic: OSA leaves many people feeling drained and lacking vitality due to constant sleep interruptions from breathing pauses at night.
- Tiredness: Those with OSA often battle persistent fatigue, hindering optimal performance and alertness throughout the day.
- Weakness: Muscle fatigue and a pervasive sense of physical weakness are common with OSA, complicating even basic tasks.
- Sleepiness in Daytime: OSA sufferers grapple with overwhelming daytime drowsiness, struggling to remain alert during daily activities.
- Loud Snoring: Disruptive snoring signals potential OSA, where airway blockages cause throat vibrations during sleep.
- Apneic Episodes: OSA’s alarming feature is brief breathing cessations during sleep, risking oxygen deprivation and sleep disruption.
- Memory Problems: Untreated OSA can detrimentally impact cognitive abilities, affecting memory retention and concentration levels.
Why Is It Important to Diagnose Sleep Apnea?
The consequences of untreated obstructive sleep apnea extend far beyond feeling tired during the day. Here are some significant health risks associated with OSA:
- Weight Gain: OSA’s disruption of sleep and metabolism can lead to increased body weight, making weight management challenging for those affected.
- High Blood Pressure: OSA’s connection to hypertension heightens the risk of cardiovascular complications like heart disease and stroke.
- Cardiovascular Disease Risk: OSA’s impact on oxygen levels and cardiovascular strain amplifies the susceptibility to heart ailments.
- Strokes: Untreated OSA escalates stroke risk due to cardiovascular stress and potential clot formation in affected individuals.
- Diabetes Type 2: OSA’s correlation with insulin resistance and glucose intolerance elevates the chances of developing type 2 diabetes.
Polysomnography Sleep Study:
Diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea typically involves a polysomnography sleep study. This comprehensive test monitors various physiological parameters during sleep, including:
- EEG Electrode: Utilizing EEG electrodes, sleep stages are tracked by analyzing brain activity, aiding in the identification of abnormal patterns during sleep.
- Pulse Oximeter: Monitoring oxygen levels in the blood, a pulse oximeter helps in detecting instances of oxygen desaturation during apneic episodes.
- Heart Monitor: With an ECG, heart rate and rhythm are continuously observed, furnishing crucial insights into cardiac function throughout sleep.
- Abdomen Check: Respiratory effort is gauged by monitoring abdominal and chest wall movements, aiding in assessing breathing patterns during sleep.
- Leg Movements: Sensors tracking leg movements identify periodic limb movements during sleep, a phenomenon often associated with obstructive sleep apnea.
Conclusion:
Obstructive sleep apnea is a common but frequently underestimated sleep condition that poses considerable risks to both physical and mental well-being. From daytime exhaustion to heightened cardiovascular threats, the untreated ramifications of OSA are substantial. Nonetheless, through timely detection and suitable intervention, individuals can enjoy marked enhancements in their well-being and overall quality of life. Should you suspect that you or a loved one may be suffering from obstructive sleep apnea, do not delay in seeking medical assistance and undergoing a thorough sleep evaluation. Prioritizing your health and welfare is paramount.

