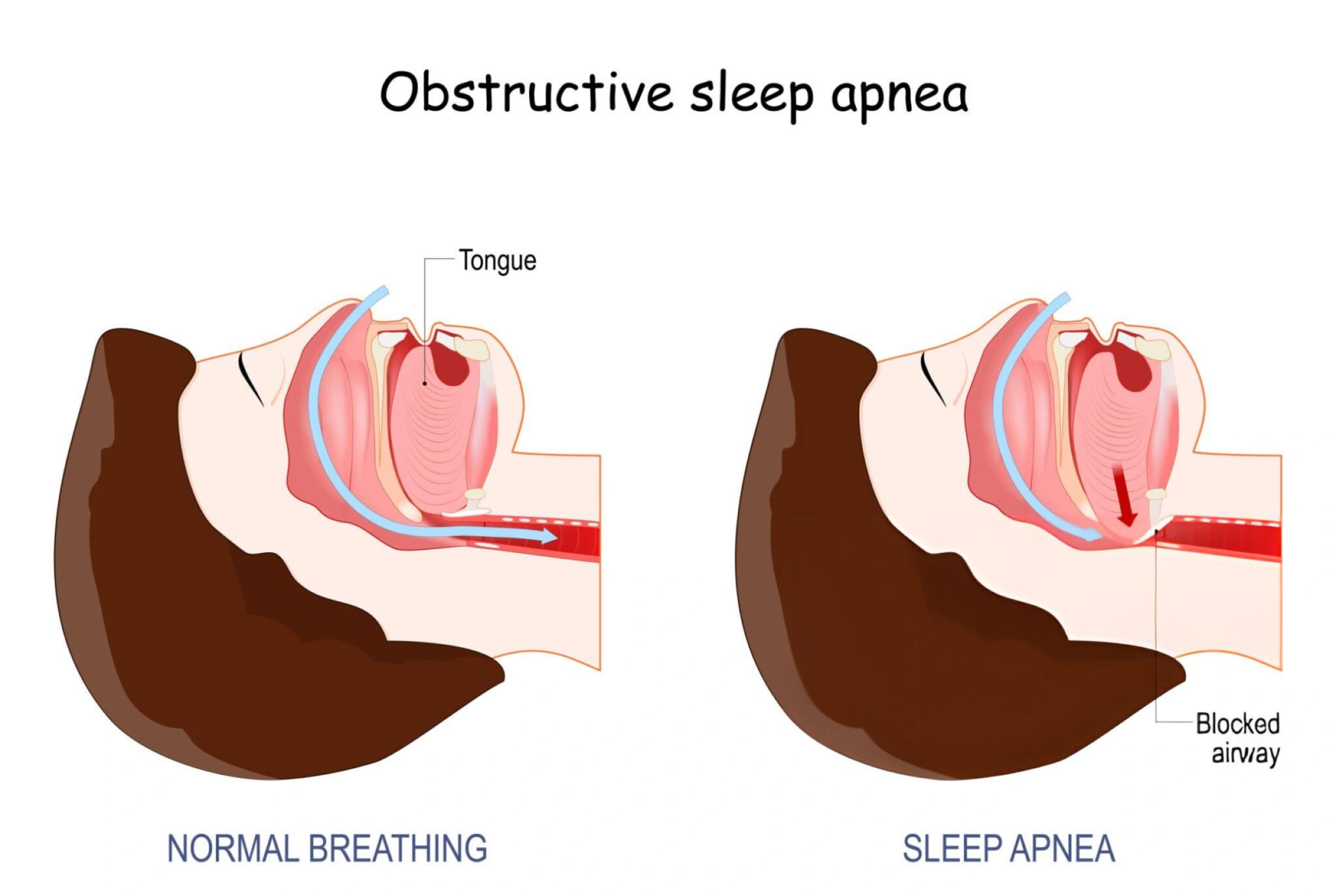
Obstructive Sleep Apnea or OSA, is a very common sleep disease characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These types of interruptions, or apneas, happen when the muscles in the throat relax vastly, which causing a temporary blockage of the airway. That�s why understanding the risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea is really important for early detection and effective treatment. And with the help of this blog, you can get complete information on all the risk factors for developing obstructive sleep apnea.
Common Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
1. Anatomical Factors
- Excess Tissue in the Throat: Having excess soft tissue around the airway can obstruct breathing, particularly when the muscles relax during sleep.
- Large Tonsils or Adenoids: Enlarged tonsils or adenoids can block the airway, especially in children, contributing to obstructive sleep apnea.
- Narrow Airway: A naturally narrow airway, which may be hereditary, can increase the risk of developing sleep apnea.
- Deviated Septum: A misalignment of the nasal septum can obstruct nasal breathing, contributing to obstructive sleep apnea.
2. Lifestyle and Behavioral Factors
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can increase the likelihood of airway obstruction during sleep. Fat deposits around the upper airway can make it difficult to breathe.
- Smoking: Smoking can increase inflammation and fluid retention in the upper airway, leading to obstructive sleep apnea.
- Alcohol Use: Alcohol relaxes the muscles in the throat, which can exacerbate airway blockage during sleep.
- Sedative Medications: Certain medications that relax the central nervous system can also relax the throat muscles, contributing to OSA.
3. Health Conditions
- Hypertension: There is a strong association between high blood pressure and OSA, although it is unclear which condition typically occurs first.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely to develop obstructive sleep apnea. The relationship between these conditions may be related to obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Heart Disease: Conditions such as congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation can be associated with a higher risk of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Chronic Nasal Congestion: Persistent nasal congestion can lead to breathing difficulties during sleep, increasing the risk of OSA.
4. Demographic Factors
- Age: The risk of obstructive sleep apnea increases with age. Although it can happen at any age of person, but it is more common in older adults.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop OSA than women, although the risk for women increases with menopause.
- Family History: Genetics play a role in obstructive sleep apnea. If you have a family history of sleep apnea, then your risk is higher of having this disease.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, and Pacific Islanders, may have a higher prevalence of OSA, possibly due to anatomical differences and higher rates of obesity.
5. Physiological Factors
- Neck Circumference: A thicker neck may indicate more soft tissue that can block the airway. Men with a neck circumference greater than 17 inches and women with a neck circumference greater than 16 inches are at higher risk.
- Retrognathia: A recessed chin or lower jaw can narrow the airway, increasing the likelihood of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Micrognathia: An abnormally small jaw can also contribute to airway obstruction during sleep.
6. Sleep-Related Factors
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on your back can cause the tongue and soft tissues to collapse to the back of the throat, leading to airway blockage.
- Fragmented Sleep: Poor sleep quality and frequent awakenings can exacerbate obstructive sleep apnea by disrupting normal breathing patterns.
- Nighttime Reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause acid to back up into the throat, leading to irritation and inflammation that can worsen OSA.
7. Hormonal Factors
- Menopause: Hormonal changes during menopause can increase the risk of OSA in women, possibly due to changes in the distribution of body fat and muscle tone.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS are at a higher risk for obstructive sleep apnea due to hormonal imbalances and higher prevalence of obesity.
8. Environmental Factors
- Allergens: Exposure to allergens can cause nasal congestion and swelling, contributing to breathing difficulties during sleep.
- Air Pollution: Poor air quality can lead to respiratory problems that may exacerbate OSA.
- Work Schedule: Irregular work hours, particularly those involving shift work, can disrupt sleep patterns and increase the risk of OSA.
Conclusion
Obstructive Sleep Apnea is a multifaceted condition influenced by a combination of anatomical, lifestyle, health-related, demographic, and environmental factors. By understanding Obstructive Sleep Apnea and its risk factors, individuals and healthcare providers can better identify those at risk and implement strategies to manage and mitigate the impact of OSA. If you suspect you or a loved one may be at risk, feel free to consult with Prof. Dr. Syed Arshad Hussin (The best pulmonologist in Dubai), for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment plan.