Pulmonary stenosis is a serious condition that restricts blood flow from the heart to the lungs, making it harder for the body to receive oxygen-rich blood. Most of the time this condition is congenital, but it can develop later as well, and that�s the reason understanding this disease can help you get the appropriate treatment at the right time.
So if you are finding the complete information on what pulmonary stenosis is, then this blog will provide you all the necessary information from how it presents itself to what options are available for treatment.
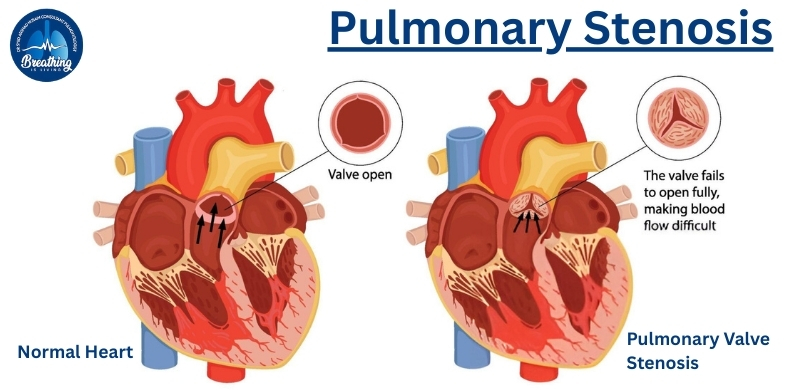
What is Pulmonary Stenosis?
Definition: Pulmonary stenosis is a condition where the flow of blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs is restricted due to narrowing of the pulmonary valve or artery.
- Type: It�s often a congenital heart defect but can also develop later in life.
? Think of it as a narrow gateway between the heart and the lungs, making the heart work harder to push blood through.
Common Symptoms of Pulmonary Stenosis
- Mild Cases: May not show any symptoms and could go undetected for years.
Moderate to Severe Cases:
- Shortness of breath during activity
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Heart murmur
- Fainting spells (in rare cases)
- Poor weight gain or bluish skin color in babies (cyanosis)
? The more severe the narrowing, the more likely symptoms are to appear�especially during physical exertion.
Related Blog: What challenges arise from living with COPD?
What Causes Pulmonary Stenosis?
- Congenital Heart Defect: Most cases are present at birth due to improper development of the heart valve.
- Rheumatic Fever: A rare cause that can damage the valve later in life.
- Carcinoid Syndrome or Tumors: May lead to valve abnormalities in adults.
- Valvular Dysplasia: Malformed or fused valve flaps causing the narrowing.
? While most cases are congenital, knowing the rare causes helps in adult diagnosis.
How is Pulmonary Stenosis Diagnosed?
- Physical Exam: Doctor might hear a heart murmur during a checkup.
- Echocardiogram: The Main test to see the structure and flow of the heart valves.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects any stress on the heart.
- Chest X-ray: Checks the size of the heart and lung congestion.
- Cardiac MRI or CT Scan: Offers detailed imaging, especially in complex cases.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Sometimes used for both diagnosis and treatment.
? Early diagnosis can prevent the heart from overworking and developing complications.
Related Blog: Biologic Therapies Changing COPD Treatment
Treatment Options for Pulmonary Stenosis
1. Monitoring (Watchful Waiting)
- When Used: In mild cases without symptoms.
- Approach: Regular follow-ups and echocardiograms to monitor changes.
? No need for immediate treatment if the heart function remains stable.
2. Balloon Valvuloplasty
- Procedure: A catheter with a balloon is inserted into the valve and inflated to widen the narrowed area.
- Best For: Children and young adults with moderate to severe stenosis.
? Minimally invasive and often very effective, especially for congenital cases.
3. Open-Heart Surgery
- When Needed: If valvuloplasty isn�t effective or in very severe cases.
- What It Involves: Replacing or repairing the pulmonary valve.
? Used as a last resort, but offers long-term relief in complex cases
4. Medications
- Purpose: Not a cure but used to manage symptoms like heart rhythm issues or fluid buildup.
- Types: Diuretics, beta-blockers, or anticoagulants (in select cases).
? Medications offer support but are not a standalone treatment.
Related Blog: Breathing Troubles? Here�s When to See a Pulmonologist
Pulmonary Stenosis in Children
- Most cases are detected in infancy or childhood during routine exams.
- Treatment success is high when diagnosed early.
- Regular pediatric cardiology visits are essential for ongoing care.
? Children with treated pulmonary stenosis can live a healthy and happy life.
Pulmonary Stenosis in Adults
- May be undiagnosed since birth and detected during adult life.
- Symptoms might appear due to aging or valve calcification.
- Requires personalized treatment based on health status.
? Even adult-onset cases can be managed effectively with modern techniques.
Living with Pulmonary Stenosis
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Limit hardworking activity if advised, manage weight, and avoid smoking.
- Heart-Healthy Diet: Helps reduce the strain on the heart.
- Regular Check-ups: Essential for lifelong monitoring, even post-treatment. Book your Appointment today in dubai.
? With the right care, many live without limitations.
Final Thoughts
Pulmonary stenosis might sound daunting, but with timely diagnosis and appropriate care, it can be managed effectively�whether in a newborn, child, or adult. The key lies in awareness, regular monitoring, and seeking the best pulmonologist immediately, like Prof. Dr. Syed Arshad Husain for better care and appropriate treatment.