Mediastinal lymphadenopathy is a condition that refers to the enlargement of lymph nodes in the mediastinum, the central part of the chest located between the lungs. This condition can occur due to various different reasons; that�s why it is important to understand its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, which is crucial for early intervention and proper management of mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
What is Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy?
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy occurs when the lymph nodes in the chest become swollen due to various underlying health conditions. While some cases are harmless and resolve on their own, others may indicate serious diseases that require medical attention from an expert pulmonologist.
Common Causes of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
Infections
- Tuberculosis, bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to swollen lymph nodes in the mediastinum.
- Histoplasmosis, a fungal infection, is another common cause.
Inflammatory Conditions
- Sarcoidosis, an inflammatory disease that leads to the formation of granulomas, often causes lymph node swelling.
- Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can also contribute.
Cancer and Malignancies
- Lymphoma (Hodgkin�s and non-Hodgkin�s lymphoma) often leads to mediastinal lymph node enlargement.
- Lung cancer and metastatic cancers spreading from other body parts can also be culprits.
Other Causes
- Certain medications and environmental factors may contribute to lymph node swelling.
- Chronic conditions like silicosis and asbestosis due to prolonged exposure to harmful substances.
Symptoms of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
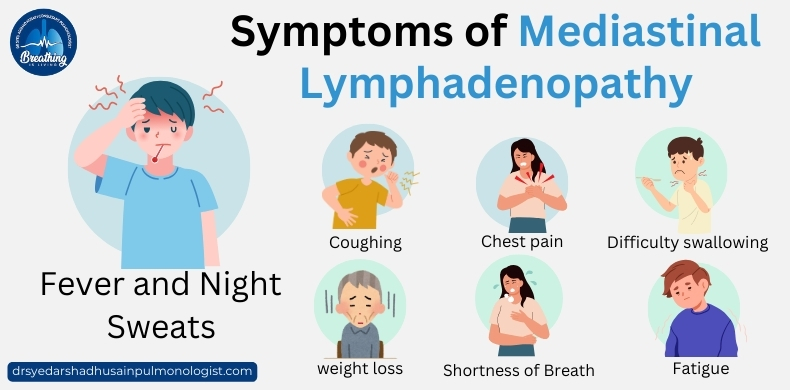
While some cases remain asymptomatic, the following symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fever and night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Difficulty swallowing (in severe cases)
Diagnosis of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
Early diagnosis is crucial to determine the underlying cause and decide on appropriate treatment options. Diagnostic tests include:
- Chest X-ray � Helps detect enlarged lymph nodes in the mediastinum.
- CT Scan or MRI � Provides detailed imaging to assess the size and location of swollen nodes.
- PET Scan � Determines metabolic activity of lymph nodes, often used for cancer evaluation.
- Bronchoscopy with Biopsy � A minimally invasive method to collect tissue samples.
- Mediastinoscopy � A surgical procedure to extract lymph node samples for analysis.
- Blood Tests � Checks for infections, inflammation, or cancer markers.
Treatment Options for Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
Treatment of mediastinal lymphadenopathy depends on the root cause of this condition:
1. Managing Infections
- Antibiotics or antifungal medications are prescribed based on the specific infection.
- Tuberculosis-induced lymphadenopathy requires a long course of anti-TB drugs.
2. Treating Inflammatory Diseases
- Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants help control conditions like sarcoidosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
3. Cancer Treatment
- Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery may be required for lymphoma or lung cancer.
- Immunotherapy and targeted drug treatments are advanced options for certain malignancies.
4. Symptomatic Relief
- Pain management, breathing exercises, and supportive care help alleviate symptoms.
- Regular monitoring for mild cases where no immediate treatment is needed.
When to Seek Medical Help?
If you experience persistent chest pain, breathing difficulties, unexplained weight loss, or prolonged fever, seek medical evaluation promptly. Early detection improves treatment outcomes, especially for infections and malignancies.
Conclusion
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy can arise from various conditions ranging from infections to cancer. Identifying the cause through proper diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. If you experience persistent symptoms, consult an expert pulmonologist like Prof. Dr. Syed Arshad Husain for timely intervention. Early diagnosis and targeted treatment can improve health outcomes and overall well-being.