Tuberculosis, often known as TB, is one of the serious infectious diseases all over the world. This very old disease is still impacting people’s health and affecting millions of people every year, and the count is on. Although there are plenty of reasons that cause TB, the most common culprit is smoking. However, smoking is not the only reason because there are plenty of other reasons too, which can develop tuberculosis.
The good news is that with awareness, early diagnosis, and the right treatment, tuberculosis (TB) is both preventable and curable. In this blog, we’ll explore what TB is, its causes, and how to identify the early warning signs.
What is Tuberculosis?
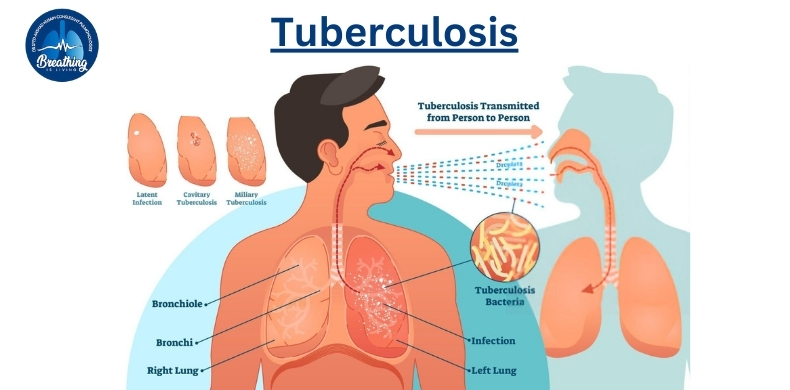
- Definition: Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, mainly affecting the lungs but can also target other parts of the body.
- Type: It can be either Latent TB (dormant, no symptoms) or Active TB (symptoms present and contagious).
✅ Think of it as a sleeping or active fire. Latent TB hides, while active TB spreads.
Is Tuberculosis Still a Global Concern?
- Yes, it’s true that TB remains a main cause of death from infectious diseases, especially in developing countries.
- According to WHO, in 2023, nearly 10.6 million people fell ill with TB globally.
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or malnutrition, are more at risk.
✅ Despite the updates in medical technology, TB remains a public health priority.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis
1. Persistent Cough (Lasting More Than 3 Weeks)
- Often the first and most obvious symptom.
- May start dry and develop into a cough with mucus or blood.
✅ A cough that doesn’t go away should never be ignored.
Related Blog: A Comprehensive Information of Chronic Cough in Adults
2. Chest Pain
- Sharp or dull pain, especially during coughing or breathing.
- Caused by lung inflammation.
✅ Chest discomfort can be an early clue, especially with other symptoms.
3. Fever and Chills
- Low-grade fever that may come and go.
- Often worse at night.
✅ Unexplained fever? TB could be the hidden culprit.
4. Night Sweats
- Soaking sweats that happen while sleeping.
- Commonly reported even in cooler climates.
✅ Frequent night sweats shouldn’t be dismissed as just stress or weather.
5. Unintentional Weight Loss
- Rapid and noticeable weight loss without dieting.
- Accompanied by fatigue and loss of appetite.
✅ Weight loss without trying may be a red flag for TB.
6. Fatigue and Weakness
- Constant tiredness, even with rest.
- May feel drained throughout the day.
✅ If rest doesn’t fix your fatigue, a TB test might be needed.
7. Swollen Lymph Nodes
- Especially around the neck or underarms.
- Could indicate TB has spread beyond the lungs.
✅ Swollen glands could mean the infection has gone systemic.
Related Blog: What challenges arise from living with COPD?
What Causes Tuberculosis?
1. Bacterial Infection
- Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a slow-growing bacteria.
- Transmitted from one person to another through airborne droplets, it happens when an infected patient coughs, sneezes, or talks.
✅ It’s airborne, making public spaces and close contact risky.
2. Weakened Immune System
- Those who are facing HIV, cancer, diabetes, or those on immunosuppressants are more vulnerable.
- Malnutrition and poor living conditions increase the risk.
✅ A weak immune system gives TB bacteria the perfect chance to grow.
3. Close Contact with TB Patients
- Spending time in poorly ventilated or crowded areas with someone who has active TB increases risk.
- Family members, roommates, and healthcare workers are more exposed.
✅ TB spreads easily in enclosed places where poor airflow is present.
4. Travel or Living in High TB Zones
- TB is a very common disease in Africa, Southeast Asia, and parts of Latin America.
- Migrants or travelers may bring TB back unknowingly.
✅ Living or working abroad in TB hotspots? Get tested regularly.
5. Age and Health Status
- Infants, young kids, and the elderly are more susceptible.
- If a person has a serious disease like kidney disease or cancer can trigger TB reactivation.
✅ The very young and very old are always at greater risk.
Related Blog: Biologic Therapies Changing COPD Treatment
How is TB Diagnosed?
- Skin Test (Mantoux Test): Checks immune response to TB bacteria.
- Blood Tests: QuantiFERON-TB Gold is common.
- Chest X-rays: Reveal lung damage or TB-related inflammation.
- Sputum Test: Checks for bacteria in coughed-up mucus.
✅ Timely diagnosis helps contain the spread and start treatment early.
Related Blog: Breathing Troubles? Here’s When to See a Pulmonologist
Can TB Be Treated?
- Yes! TB is curable with a strict antibiotic regimen that will last 6–9 months.
- Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) is often used to ensure patients take their medications properly.
- Drug-resistant TB may need stronger and longer treatments.
✅ Following the full course of medication is the only way to beat TB.
Who Should Be Extra Cautious?
- Healthcare workers, caregivers, or anyone around TB patients.
- People with HIV or on immune-suppressing medication.
- Those who live in or travel to high-risk areas.
✅ If you’re in a high-risk group, regular screening is vital.
Final Thoughts
Tuberculosis is still around, but it’s no longer a mystery. With the right information, proactive healthcare, and early intervention, it can be controlled and cured. If you or someone you know shows signs of TB, don’t delay—seek medical help in dubai, UAE from the best pulmonologist like Prof. Dr. Syed Arshad Husain for the best care and treatment.
Prevention starts with awareness. And treatment begins with action.